网络架构与七层参考模式
Applications
Most people konw about the Internet(a computer network) through applications
- World Wide Web
- On line games
- Email(Gmail, hotmail,...)
- Online Social Network(Facebook, Twitter,...)
- Streaming Audio Video (Youbute, pptv, kkbox, ppstream,...)
- File Sharing(dropbox,...)
- Instant Messaging(Skype, IM+, MSNLine, WeChat,...)
A multimedia application including video conferencing.
URL
Uniform Resource Locater, http://domain.ltd
- HTTP
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
- 17 messages for one URL request
- 6 to find the IP(Internet Protocol) address
- 3 for connection establishment of TCP
- 4 for HTTP request and acknowledgement
- Request: I got your request and I will send the data
- Reply: Here is the data you requested; I got the data
- 4 messages for tearing down TCP connection
Network Connectivity
Important terminologies
- Link(电脑与电脑连接的)
- Nodes(电脑,手机等设备)
- Point-to-point(点对点)
- Multiple access(多个设备同事存取link)
- Switched Network
- Circult Switched(电路交换)
- Packet Switched(分组交换)
- Packet, message 分组数据,message原始资料
- Store-and-forward 分包存储和转送,手->查表->转送
Terminologies(contd.)
- Hosts
- Switches
- Spanning tree 生成树
- internetwork 互联网
- Router/gateway
- Host-to-host connectivity
- Address
- Routing
- Unicast/broadcast/multicast
- LAN(Local Area Networks)
- MAN(Metropolitan Area Networks)
- WAN(Wide Area Networks)
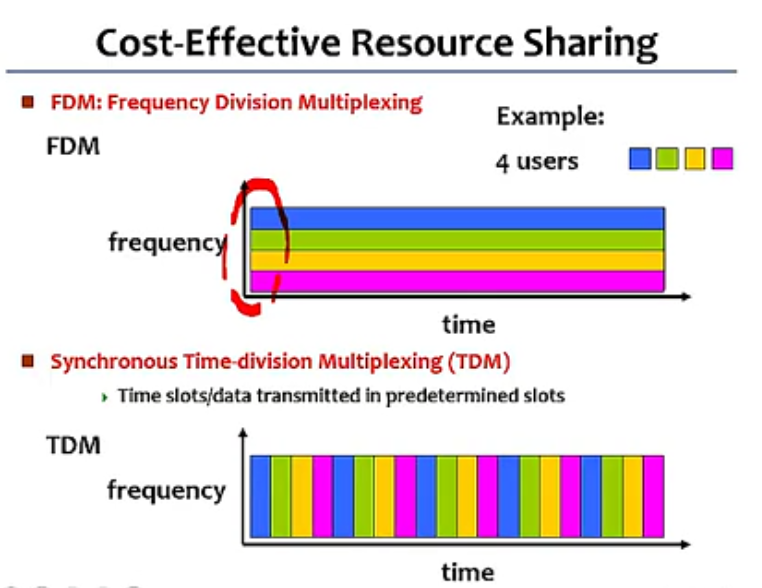
Cost-Effective Resource Sharing
- Resources: links and nodes
- How to share a link?
- Multiplexing
- FDM:Frequence Division Multiplexing
- frequency(平带)/time
- TDM: Synchronous Time-division Multiplexing
- Time slots/data transmitted in predetermined slots
- frequency/time
- FDM:Frequence Division Multiplexing
- De-multiplexing
- Multiplexing
- Statistical Multiplexing
- Data is transmitted based on demand of each flow.
- What is a flow?
- Packets vs. Messages
- FIFO(Queue), Round-Robin(轮循), Priorities(优先权 Quality-of-Service(QoS) 服务质量)
- Congested? 拥挤的
Logical Channels
- Logical Channels
- Application-to-Application communication path or a pipe
Network Reliability
- Network should hide the errors
- Bits are lost
- Bit errors(1 to a 0, and vice versa)
- Burst errors - several consecutive errors
- Packets are lost(Congestion)
- Links and Node failures
- Messsages are delayed
- Messages are delivered out-of-order
- Third parties eavesdrop
Network Architecture
- Application Programs
- Process-to-process Channels
- Host-to-Host Connectivity
- hardware
protocols
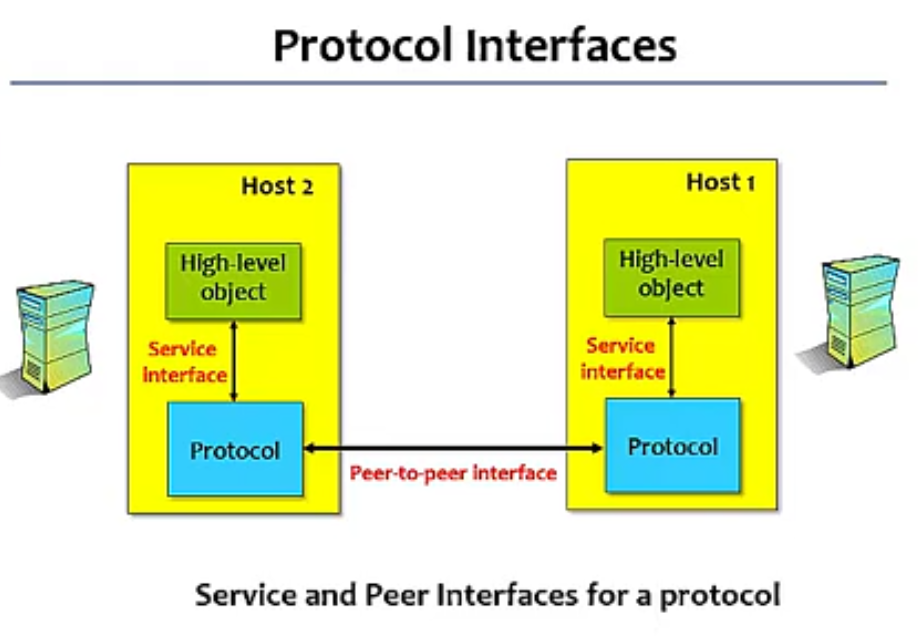
- Protocol defines the interfaces between
- the layers in the same system and with
- the layers of peer system
- Building blocks of a network architecture
- Each protocol ojbect has two different interfaces
- Service interface: operations on this protocol
- Peer-to-peer interface: message exchanges with peer
- Protocol Specification: pseudo-code, state transition diagram, message format
- Interoperable: when two or more protocols that implement the specification accurately
- IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force
- Define Internet standard protocols
Encapsulation
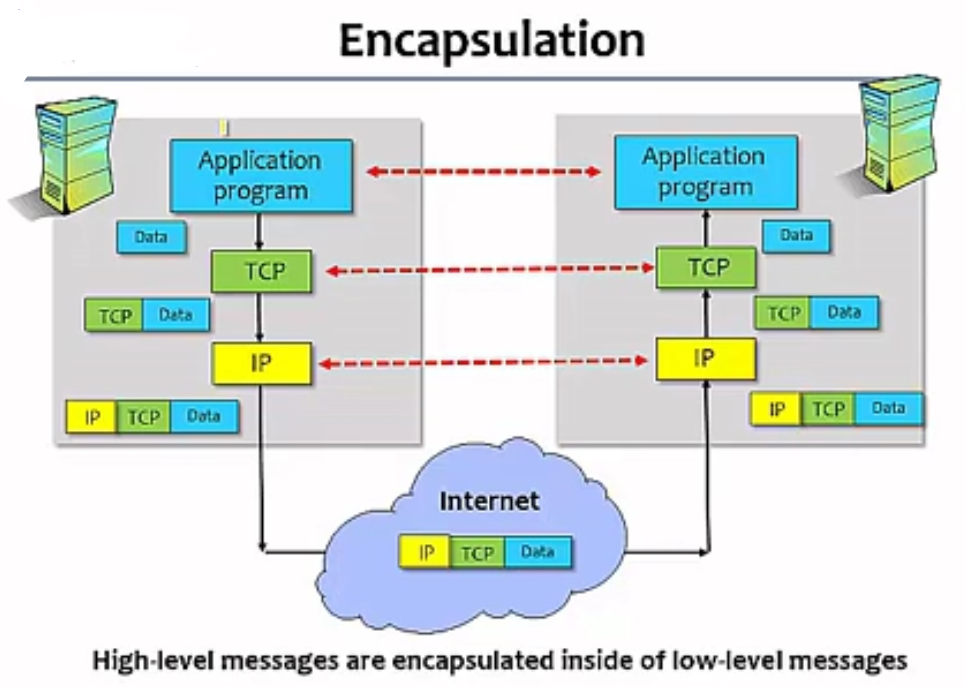
OSI Architecture
OSI: Open System Interconnection
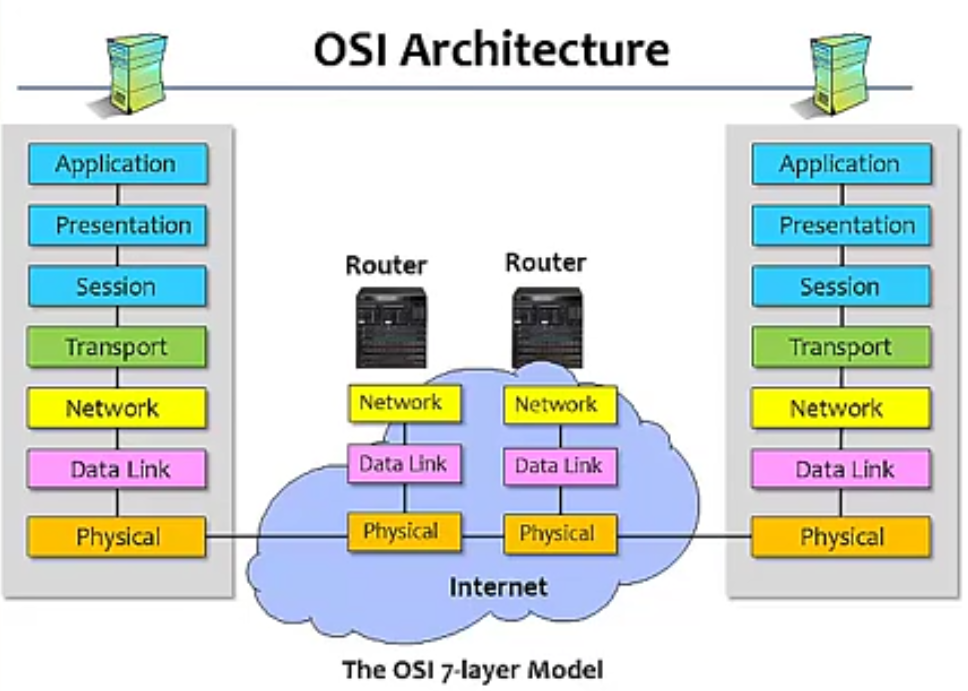
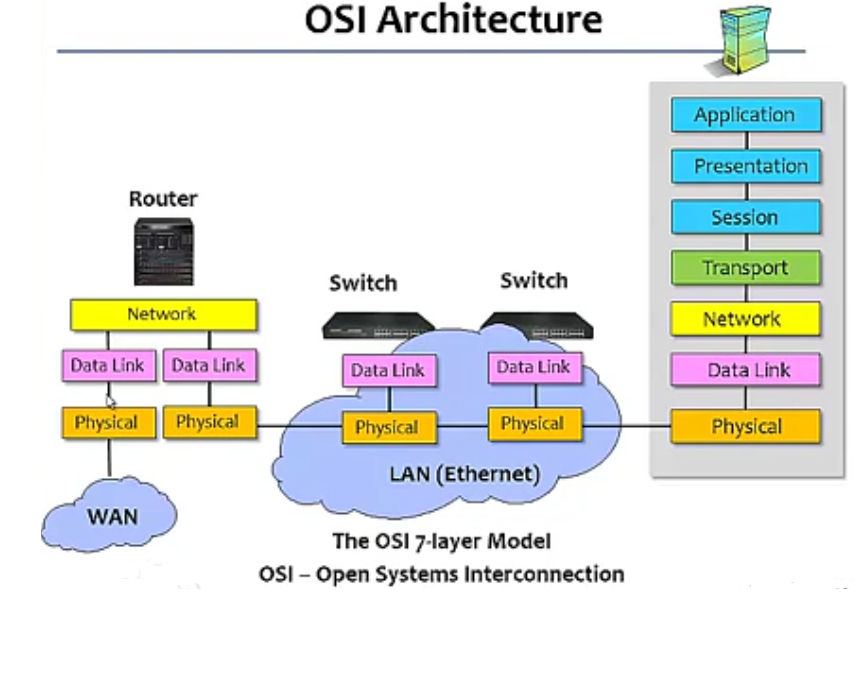
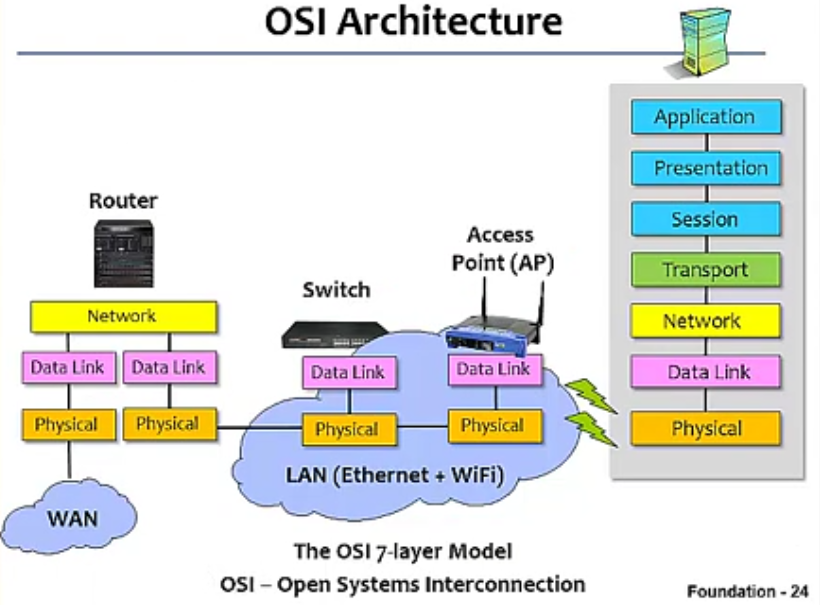
Description of Layers
Physical Layer(如何将原始资料在 Link 上传输)
- Handles the transmission of raw bits over a communication link
- Coaxial cable 同轴线
- Twisted pair 双绞线

- Optical Fiber 光纤 (不受电磁波干扰)
- Air space(wireless radio channel) 无线网路(电磁波传输)
- Coaxial cable 同轴线
- Different Signal Coding schemes
- 同轴线和双绞线容易受电磁波干扰
- Handles the transmission of raw bits over a communication link
Data Link Layer(如何将 frame 传给直接相连的主机或设备)
- Collects a stream of bits into a frame
- How to transmit a frame to a directly conencted hsot(destination)
- MAC (Meda Access Control Protocol)
- CSMA/CD (IEEE 802.3 Ethernet)
- CSMA/CA (IEEE 8.2.11 Wireless LAN)
- Layer 2 devices
- Switches
- Bridges
Network Layer(如何将封包透过 internet 送给目的主机 )
- How to transmit frames to a host via the Internet?
- Handles routing among nodes within a packet-swiched network
- Data exchanged between nodes in this layer is called a packet
- IP protocol
- Routers
- Routing protocols
- RIP
- OSPF
- BGP
- Routing Tables
Transport Layer(提供不同主机 processes 之间的资料传送)
- implements a process-to-process channel
- unit of data exchanges in this layer is called a message
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - Reliable service
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - Unreliable service
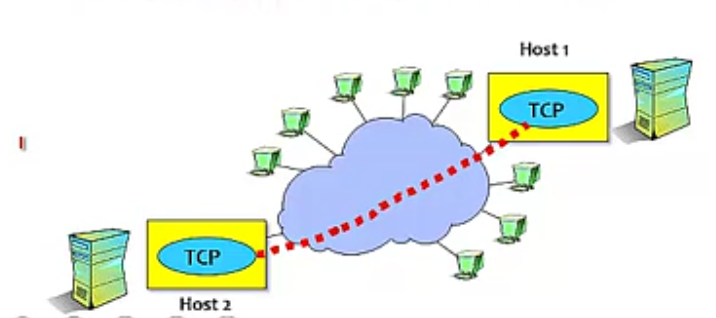
Session Layer
- Provides a name space that is used to tie together the potentially different transport streams that are part of a single application
Prensentation Layer
- Concerned about hte format of data exchanged between peers
Application Layer
- Standardize common type of exchanges
- FTP/E-mail/DNS/HTTP/Browsers/FB
Network Performance
- Defined by IETF
- Three main features
- Does not imply strict layering. The application is free to bypass the defined transport layers and to directly use IP or other underlying networks.
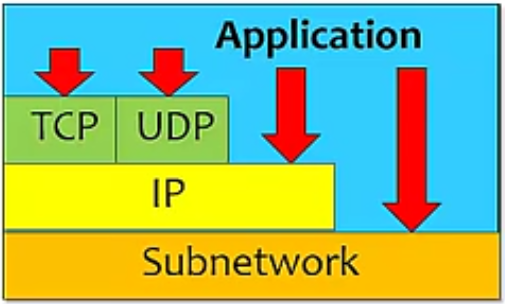
- Bandwidth
- Width of the frequency band
- Number of bits per second that can be transmitted over a communication link
- 1 Mbps: 1 x 10^6 bits/second
- 1 x 10^-6 seconds to transmit each bit or imagine that a timeline, now each bit occupies 1 micro second space.
- On a 2 Mbps link the width is 0.5 micro second.
- Smaller the width more will be transmisson per unit time.
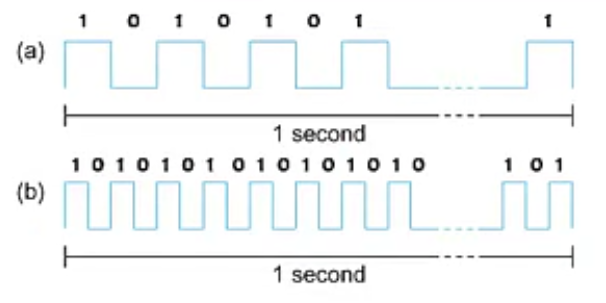
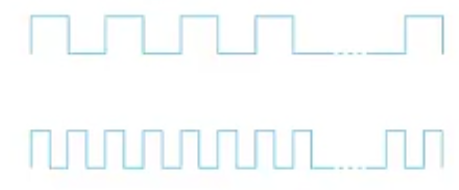
Bits transmitted at a particular bandwidth can be regarded as having some width:
a. bits transimitted at 1Mbps (each bit 1 us wide)
b. bits transmitted at 2Mbps(eacg bit 0.5 us wide)
Latency = Propagation time + transimission time + queuing time(排队时间)
Propagation time = distance/speed of light
Trasmission time = size/bandwidth
one bit transmission => propagation is important (短资料很快就送完,但需要长时间才能传到对方,资料已送完,但签到资料还未到达对方) Propagation time >> transmission time
Large bytes transmission => bandwidth is important (长资料很慢才能送完,未送完前,前导资料已到对方) Transmisson time >> propagation time
Delay X Bandwidth
- The channel between a pair of processes can be viewed as a pipe
- Latency(delay): length of the pipe
- Bandwidth: width of the pipe
- Delay x Bandwidth means how many data can be stored in the pipe
- For example, delay of 80 ms and bandwidth of 100 Mbps
80 x 10^3 seconds x 100 x 10^6 bits/second
8 * 10^6 bits = 8 Mbits = 1MB data

- Relative importance of bandwidth and latency depends on application
- For large file tansfer, bandwidth is critical
- For small messages(HTTP, NFS, etc.), latency is critical
- Variance in latency(jitter) can also affect some applications(e.g., audio/video conferencing)
Ethernet
Introduction Ethernet
- Most successfull local area networking technology of last 30 years.
- First widely used LAN technology
- Kept up with speed race: 10 Mbps - 100 Gbps
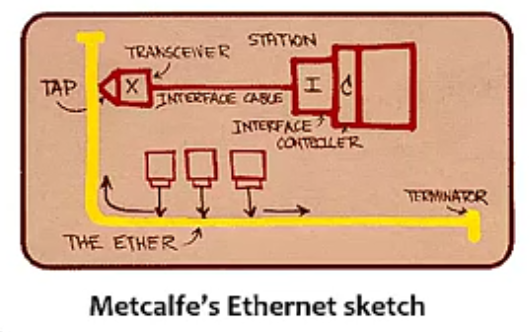
Developed in the mid-1970s by researchers at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Centers(PARC)
DEC and Intel joined Xerox to define a 10-Mbps Ethernet standard in 1978.
This standard formed the basis for IEEE standard 802.3
More recently 802.3 has been extended to include
- 100-Mbps version called Fast Ethernet
- 1000-Mbps version called Gigabit Ethernet
- 10 Gibabit Ethernet, and also
- 100 Gibabit Ethernet
Connectionless: No handshaking between sending and receiving NICs
Unreliable: receiving NIC doesn't send ACKs or NACKs to sending NIC
Ethernets' MAC protocol: Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Bus topology popular throught mid 90s(总线拓扑)
- all nodes in same collision domain(can collide with each other)